3D hologram projectors are a fascinating blend of art and technology, bringing digital images to life in three-dimensional forms. They have applications in various fields, from entertainment and advertising to education and medicine. Understanding how these projectors work can provide insight into their potential uses and future developments. This article will delve into the technology behind 3D hologram projector, covering the principles of holography, components, types, applications, and future trends.
What is Holography?
The Basics of Holography
Holography is a photographic technique that records the light scattered from objects and reconstructs it in such a way that it appears three-dimensional to the observer. This process involves capturing the interference pattern of light waves using a laser. Unlike traditional photography, which captures a flat image, holography collects data on both the intensity and the phase of light.
The result is a hologram, which can be viewed as a three-dimensional representation of the object. The unique feature of holograms is their ability to represent light fields, and when viewed from different angles, they appear to exhibit depth. This quality sets holography apart from conventional imaging methods.
Creating a Hologram
To create a hologram, a coherent light source, usually a laser, illuminates the object to be recorded. The laser beam splits into two paths: the object beam and the reference beam. The object beam reflects off the object, while the reference beam directly hits the recording medium. The interference pattern generated by the combination of these two beams is recorded on a sensitive surface.
After development, when the hologram is illuminated with coherent light, it reconstructs the light field of the original scene, allowing viewers to see the three-dimensional image. This process highlights how holography captures data beyond the surface, making it ideal for creating intricate 3D images.

Key Components of a Hologram Projector
Light Sources
One of the primary components of a hologram projector is the light source. High-quality lasers, especially those with coherent output, are often used due to their ability to produce clear and focused light waves necessary for creating and displaying holograms. Various wavelengths may be employed depending on the intended application or aesthetic goal.
Some modern hologram projectors may also use LED-based light sources. Though not as coherent as lasers, high-intensity LEDs can produce vibrant and colorful holograms, allowing for greater versatility in design. The choice of light source directly impacts the quality, color, and clarity of the projected holographic image.
Projection Systems
The projection system is another critical component that determines how the holographic images are displayed. This can range from simple systems that utilize reflective surfaces to advanced, multi-layered systems capable of projecting 3D images in real time. Advanced holographic projectors employ special optics to manipulate light and enhance image quality, resulting in sharper and more vivid holograms.
Some projectors utilize holographic displays created with liquid crystal displays (LCD) or digital light processing (DLP). These systems rely on micro-mirrors or pixels to represent the interference patterns necessary for creating lifelike holograms. The sophistication of these systems often correlates with the projector’s size, price, and application.
Types of Hologram Projectors
Static Hologram Projectors
Static hologram projectors are designed to display fixed holographic images. These projectors are commonly used for promotional displays, artwork, or educational exhibits. They provide a powerful visual impact, allowing viewers to engage with the holographic content from various angles. Static holograms are often used in museum exhibits to provide a unique perspective on historical artifacts as well.
Because static holograms do not require real-time data updates, they tend to be simpler and more cost-effective than their dynamic counterparts. They can be displayed in strategic locations to draw attention to specific products or ideas without needing constant supervision or maintenance.
Dynamic Hologram Projectors
Dynamic hologram projectors are more advanced and versatile, capable of displaying moving images in 3D. These projectors are increasingly popular in entertainment and advertising, offering immersive experiences in concerts, trade shows, and theme parks. Dynamic holograms can create a sense of movement that captures audience attention and provides a memorable visual experience.
Using high-speed processing and complex algorithms, dynamic hologram projectors can manipulate light in real time to display animations or video content. This versatility allows businesses and organizations to engage customers effectively, providing an interactive element that static holograms cannot offer.
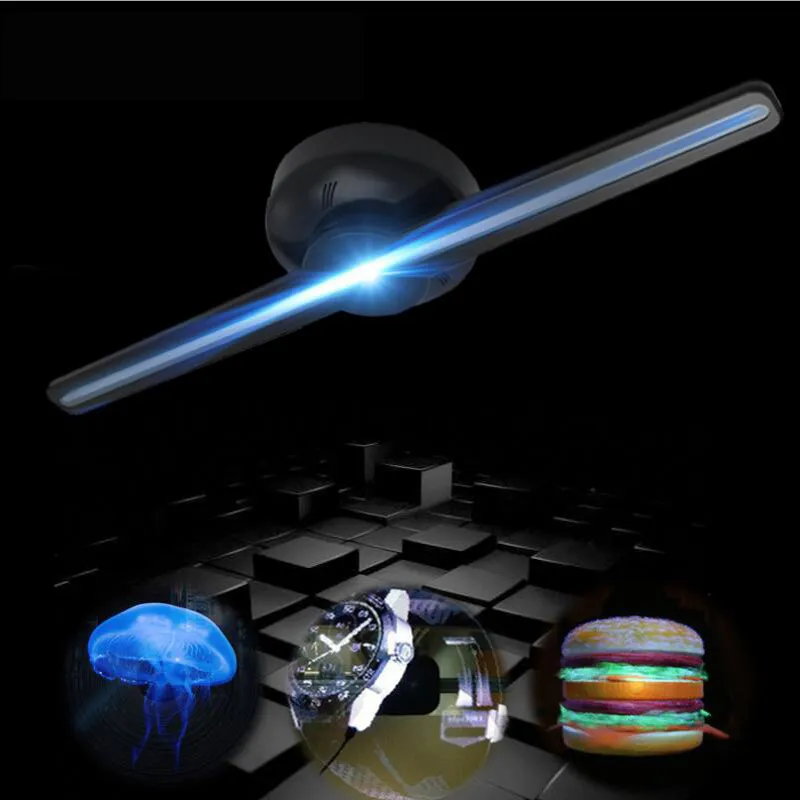
Applications of 3D Hologram Projectors
Entertainment and Events
One of the most exciting applications of 3D hologram projector is in the entertainment industry. Concerts and festivals increasingly utilize holographic technology to create stunning visuals, such as bringing deceased artists back for memorable performances or enhancing stage designs. By generating lifelike projections, these events offer audiences a unique and unforgettable experience.
Additionally, holograms serve as dynamic backdrops for theater productions and performances. Combining holograms with live action creates immersive storytelling experiences, allowing audiences to engage with the artistic vision in new and compelling ways.
Education and Training
Hologram projectors are also making waves in education. They can provide interactive teaching tools that bring complex concepts to life, making learning more engaging for students. For example, medical schools can use 3D holograms to demonstrate anatomy, allowing students to visualize organs and systems in three dimensions.
In corporate training environments, holograms can facilitate technical training sessions by simulating real-world scenarios. This approach helps employees understand challenging procedures and practices without the risks associated with hands-on training. Holographic training tools can enhance retention and boost confidence in learners, fostering a deeper understanding of the material.
Future Trends in Holographic Technology
Advancements in Display Technology
As technology advances, so do the capabilities of 3D hologram projector. Researchers are constantly developing new display technologies to improve the quality and resolution of holograms. For instance, advancements in micro-display technology may lead to compact projectors that deliver stunning visuals without requiring large devices.
Additionally, the integration of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) will likely enhance holographic experiences, creating multipurpose tools for entertainment, training, and communication. As these technologies convergently evolve, users will have access to more immersive and engaging experiences.
Increased Accessibility
Holographic technology remains relatively costly and niche. However, as advancements occur and manufacturing techniques improve, more affordable hologram projectors may emerge. This would allow smaller businesses and individuals to adopt holographic displays for advertising, marketing, or simply for personal enjoyment.
Increased accessibility can lead to widespread adoption across various sectors, transforming how we communicate, educate, and entertain ourselves. The future of holographic technology holds the potential for widespread use, making it an integral part of modern visual culture.

Overcoming Challenges in Holographic Projection
Addressing Technical Limitations
While holographic technology offers exciting possibilities, it still faces technical challenges. One significant issue is the limited viewing angle; holograms often appear distorted or fade when viewed from certain angles. Researchers continue to investigate ways to improve viewing angles and ensure that holograms maintain their integrity, regardless of the viewer’s position.
Moreover, achieving higher resolution holograms requires advanced processing capabilities and better data handling techniques. As the need for clearer and more detailed images grows, advancements in optics, algorithms, and display technology will play a pivotal role in overcoming these limitations.
Tackling Environmental Constraints
Holographic displays can also struggle with environmental influences, such as ambient light. Proper lighting conditions are necessary to ensure that holograms appear vivid and clear. Developers are working on solutions to mitigate these challenges, including adaptive lighting systems that can help optimize the visibility of holograms in various settings.
Additionally, integrating AI and machine learning may improve adaptability in real-time environments. By analyzing surroundings and adjusting lighting accordingly, projectors may enhance the user experience and ensure the ideal viewing conditions for holographic content.
Embracing the Future of Holography
The technology behind 3D hologram projector represents a unique intersection of innovation and creativity. From understanding holography to exploring the myriad applications, the potential for this technology is immense. As advancements in display technologies continue, we can expect exciting developments that enable better, more accessible holographic experiences.
Familiarity with how hologram projectors work empowers individuals and organizations to leverage their capabilities effectively. Whether you’re looking to enhance your presentations, engage customers, or provide immersive educational experiences, understanding the technology behind 3D hologram projector positions you to utilize this powerful tool in imaginative ways. The future of holography is bright, and embracing it opens doors to new possibilities we’ve only begun to explore.



